Automotive Cooling System |San Jose, CA
Is your vehicle overheating or leaking coolant? Don’t worry, Akin’s auto repair can efficiently determine the issue with your cooling system to get you back on the road as soon as possible. We offer radiator replacements, Cooling hose and heater hose replacements, thermostat, water pump as well as electronic cooling system issues such as cooling fan switches, relays, cooling fans, broken or shorted wire repair for the cooling system. Trust Akins Auto Repair with your next auto coolant repair. Contact us in San Jose
Cooling System
Trust Akins Auto Repair with your next auto coolant repair. Contact us in San Jose
The cooling system helps regulate the amount of heat in the engine.
Your car’s engine runs most efficiently at a relatively high and steady temperature. If it’s too hot, the engine can overheat. If it’s too cold, the engine emits more pollutants, and components prematurely wear out. If the cooling system fails to keep the engine at the right temperature, it can suffer significant damage and in some cases, fail entirely.
Antifreeze can leak from your car:
- At the radiator: The most common source of leaks is your radiator itself. Many modern radiators have an aluminum core (the tubes and fins) and crimped-on plastic tanks. Older vehicles may have welded aluminum tanks, while even older cars might have a copper radiator. In all cases, a leak can occur at any of the joints in the radiator itself or where the tanks connect to the radiator.
- At the reservoir and hoses: Antifreeze leaks are also common at the various connections between your rubber hoses and the engine, antifreeze reservoir, heater core, thermostat housing or radiator. Over time, hoses can get hard and brittle, and clamps can loosen slightly, allowing antifreeze to leak out. Some of these are easy to inspect, while others are difficult to access and inspect from under the hood.
- At the head gasket: This is one of the most troubling locations for an antifreeze leak. Often when a cylinder head gasket leak starts, it’s not long before you have major coolant loss. And while it’s bad enough if the coolant leaks outside of your engine, if it leaks inside, you will see a reduction in power, increased emissions and the potential for major engine damage due to mixing oil and coolant.
Related Services & Repairs
automotive-cooling-system-info graphic-diagram
- Coolant Expansion Tank
- Cooling Fan Motor
- Cooling Fan Assembly
- Heater Blower Motor
- Heater Core
- Radiator
- Radiator hose – lower
- Radiator hose – upper
- Thermostat
- Water Pump
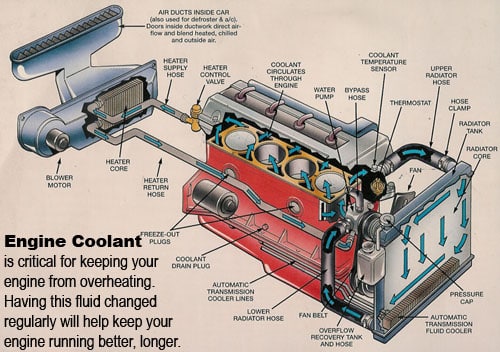
Although a few cars are air-cooled, most modern vehicles use liquid cooling. Here are the critical components in liquid-cooled systems.
Coolant, or antifreeze, performs two critical function: keeping radiator fluid from freezing in wintry conditions and keeping the engine from overheating in the summer. Coolant is composed of 50 percent ethylene glycol and 50 percent water, which helps raise its boiling point and lower its freezing point. Corrosion inhibitors protect vital metallic cooling system components from corroding, and silicates lubricate seals. There are different kinds of antifreeze, which are most easily identified by their color. How do they differ?
“The green stuff” is the traditional coolant, which can be used in most cars. It contains lubricating silicates and corrosion inhibitors, but these silicates deteriorate rather quickly, requiring coolant changes every 2 years or 24,000 miles.
Coolant can also be red, yellow, orange, or even purple. Most coolants not green in color are similar: they are simply dyed different colors. They have a longer claimed service life, thus requiring fewer fluid changes—in some cases up to 100,000 miles. Refer to your owner’s manual for details on your car’s coolant requirements.
The radiator is a heat exchanger with hundreds of individual tubes and fins that reduce the temperature of the coolant. As coolant travels through the engine passageways, it absorbs and removes heat from the engine, transporting it to the radiator. Air flows through the coolant passages as the car moves, cooling the tubes and fins, and coolant reenters the engine with a reduced temperature.
Radiator cap. If you’ve ever worked on a car, then you know not to remove the radiator cap while the engine is warm. That’s because the cap is a pressure-release valve. It also keeps the cooling system under pressure to increase the boiling point of coolant.
The engine, or radiator, fan can be driven by a drive belt or an electric motor. It helps cool a car when it is stationary or moving slowly.
The thermostat helps the engine reach operating temperature by preventing coolant from circulating to the radiator, thus allowing the engine to heat up more quickly. As the engine reaches operating temperature, the thermostat opens and allows coolant to flow through the radiator.
The water pump circulates coolant through the system via an impeller (a rotor that spins to move fluid) that is driven by a belt.
The heater core is a smaller version of the radiator located underneath the dashboard. A motor blows air past the heater core, which transfers heat to the air. This keeps cabin occupants warm even in winter.
Transmission cooler. In addition to keeping the engine cool, on cars with an automatic transmission the radiator is equipped with a separate heat exchanger to keep transmission fluidfrom boiling over.
If your car is leaking coolant, immediately determine from where and how much. If it continues to leak, schedule your car for service as soon as pos
Services
Electrical
- Battery
- Alternator
- Starter
- Charging System
- Lights
- Instruments
Drive Train
- Transmission
- Differential SERVICE
- Wheel Bearings
- CV Joints
- Steering System
- Transmission
- Torque Converter
- Bearing Lube
- Steering Fluid
COOLANT LEAK
Is your radiator leaking? Is your radiator overheating? Are you running low on coolant? If you are experiencing these or any other radiator problems, come into Akins Auto Repair for a Cooling System Diagnostic.
During a Cooling System Diagnostic, one of our experienced tire and automotive service professionals will:
- Pressurize the cooling system to check for leaks
- Perform an engine block test
- Visually inspect for coolant leaks
- Check all radiator hoses
- Check the water pump and belts
- Check the thermostat and cooling fan
Miscellaneous
- Wipers
- Washers
- Tires
- Cabin Air Filter
- Engine Oil
- Antifreeze
- Freon ( A/C recharge r134)
- Brake Fluid
Suspension
- Brakes
- ABS System
- Shocks
- Struts
- Wheel Bearings
- Alignment ( SUBLET ONLY )
Engine
- Heat & Cooling
- Air Conditioning
- Belts & Hoses
- Timing Belt
- Exhaust System
- Emission System


 Please call for an appointment. Our services are not always available. For (walk in) we are extremely busy. Thank you.
Please call for an appointment. Our services are not always available. For (walk in) we are extremely busy. Thank you.